

SOLUTIONS / ENGINEERED SYSTEMS / ELECTRICAL TECHNICAL DATA
Hydrotech isn't just a distributor of quality industrial parts. We staff a full engineering department with experienced experts ready to design, assemble and integrate full system solutions.
Hydrotech isn't just a distributor of quality industrial parts, We staff a full engineering department with experienced experts ready to design, assemble and integrate full system solutions.
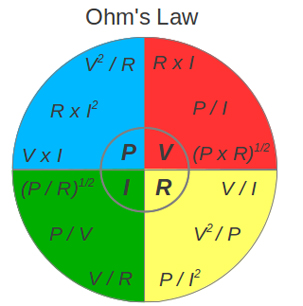
P = V I (1a)
P = R I2 (1b)
P = V2/ R (1c)
where
P = power (Watts)
V = voltage (Volts)
I = current (Amperes)
R = resistance (Ohms)
Ohms law can be expressed as:
V = R I (4a)
V = P / I (4b)
V = (P R)1/2 (4c)
A 12 volt battery supplies power to a resistance of 18 ohms.
I = (12 Volts) / (18 ohms)
= 0.67 Ampere
I = V / R (2a)
I = P / V (2b)
I = (P / R)1/2 (2c)
R = V / I (3a)
R = V2/ P (3b)
R = P / I2 (3c)
μ = 746 Php / Pinput_w (5)
where
μ = efficiency
Php = output horsepower (hp)
Pinput_w = input electrical power (Watts)
or alternatively
μ = 746 Php / (1.732 V I PF) (5b)
P3-phase = (V I PF 1.732) / 1,000 (6)
where
P3-phase = electrical power 3-phase motor (kW)
PF = power factor electrical motor
I3-phase = (746 Php) / (1.732 V μ PF) (7)
where
I3-phase = electrical current 3-phase motor (Amps)
OUR PURPOSE
American industry has never enjoyed more opportunity than it does today – or faced more challenges. Hydrotech is here to help you compete, evolve, lead and win with superior solutions in fluid power, automation, service & repair and connected technologies.